J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6481-6483.
How Far Can a Sodium Ion Travel within a Lipid Bilayer?
FranÇois Otis, Charles Racine-Berthiaume and Normand Voyer

Abstract
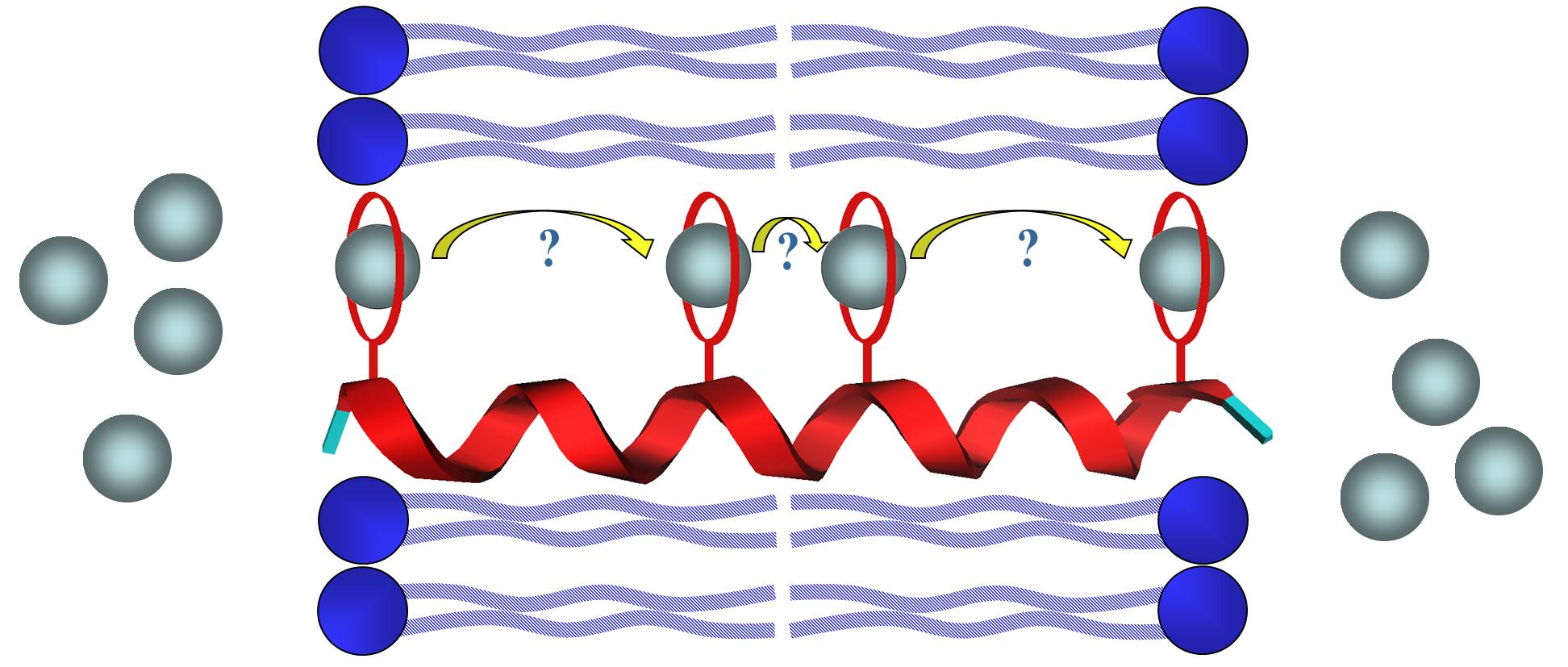
Analogues of a synthetic ion channel made from a helical peptide were used to study the mechanism of cation translocation within bilayer membranes. Derivatives bearing two, three, four, and six crown ethers used as ion relays were synthesized, and their transport abilities across lipid bilayers were measured. The results showed that the maximum distance a sodium ion is permitted to travel between two binding sites within a lipid bilayer environment is 11 Å.
Graphical abstract:
.
Article dans Le Fil des Évènements ![]()
Résumé des travaux dans Contact ![]()