ACS Omega, 2022.
Chemical Characterization of the Volatilome of Tuber canaliculatum Harvested in Quebec, Canada
David Fortier, Jean-Christophe Seguin, and Normand Voyer
Abstract
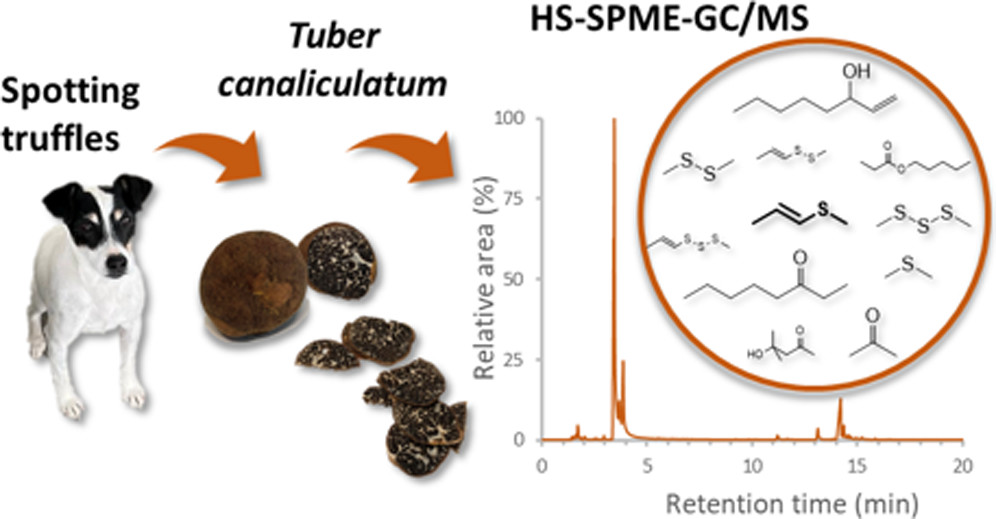
The first detailed characterization of volatile compounds from Tuber canaliculatum, a truffle newly grown in Quebec, Canada, was performed with headspace solid phase microextraction (HS-SPME) coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC/MS). A total of 30 compounds were identified, making up more than 98% of the volatile extract. The volatilome of T. canaliculatum is dominated by (E)-1-methylthio-1-propene, (Z)-1-methylthio-1-propene, dimethyl disulfide, and 1-octen-3-ol. It also includes six compounds identified for the first time in truffles, namely, 4-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-pentanone, pentyl propanoate, (Z)-1-methyl-2-(prop-1-en-1-yl)disulfide, (E)-1-methyl-2-(prop-1-en-1-yl)disulfide, (Z)-1-methyl-3-(prop-1-en-1-yl)trisulfide, and (E)-1-methyl-3-(prop-1-en-1-yl)trisulfide. With the growing interest in gastronomy in truffles in North America, it is becoming important to gather knowledge for identification purposes and to delineate the key volatile compounds responsible for the aroma of North American truffles, especially the newly harvested T. canaliculatum.